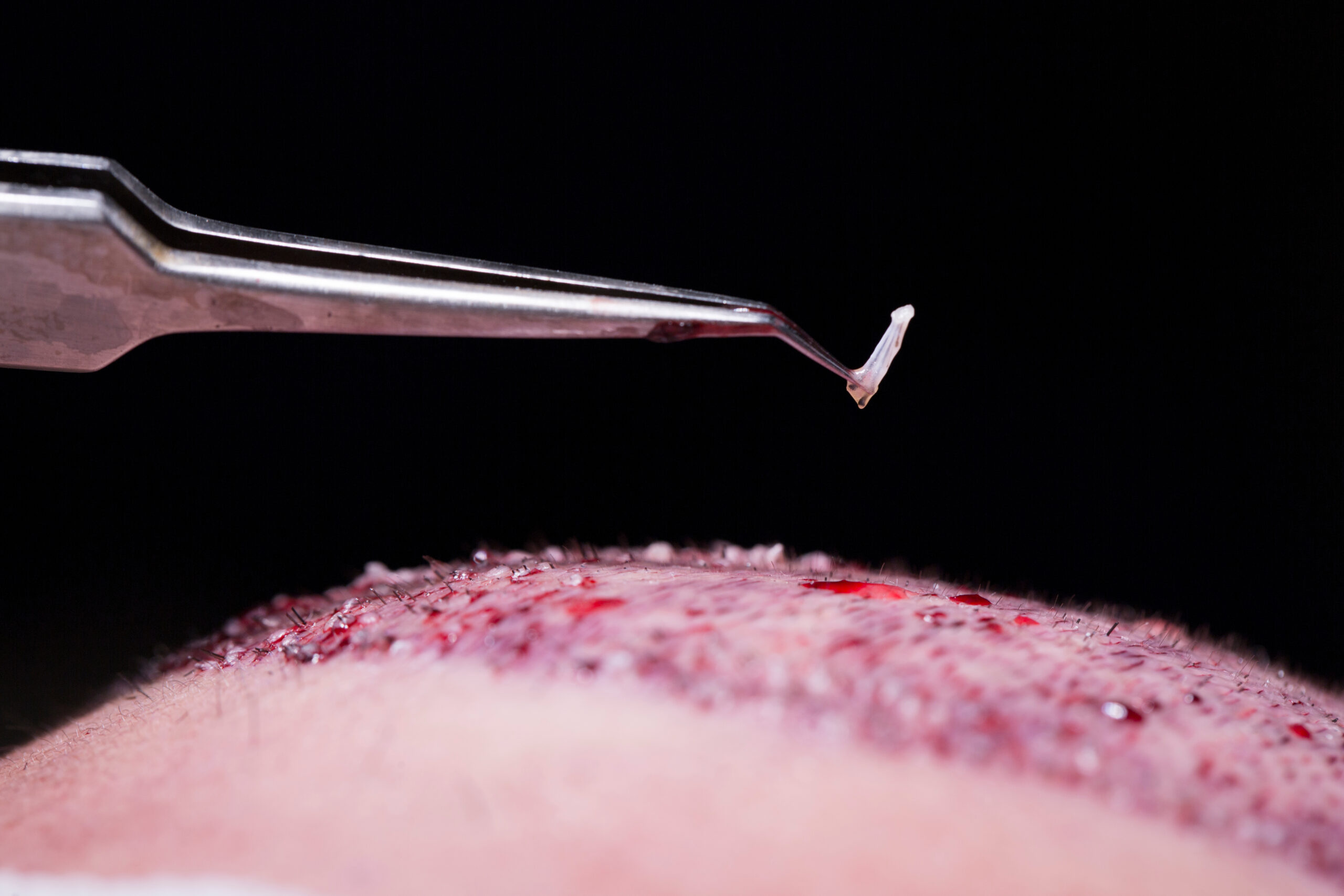
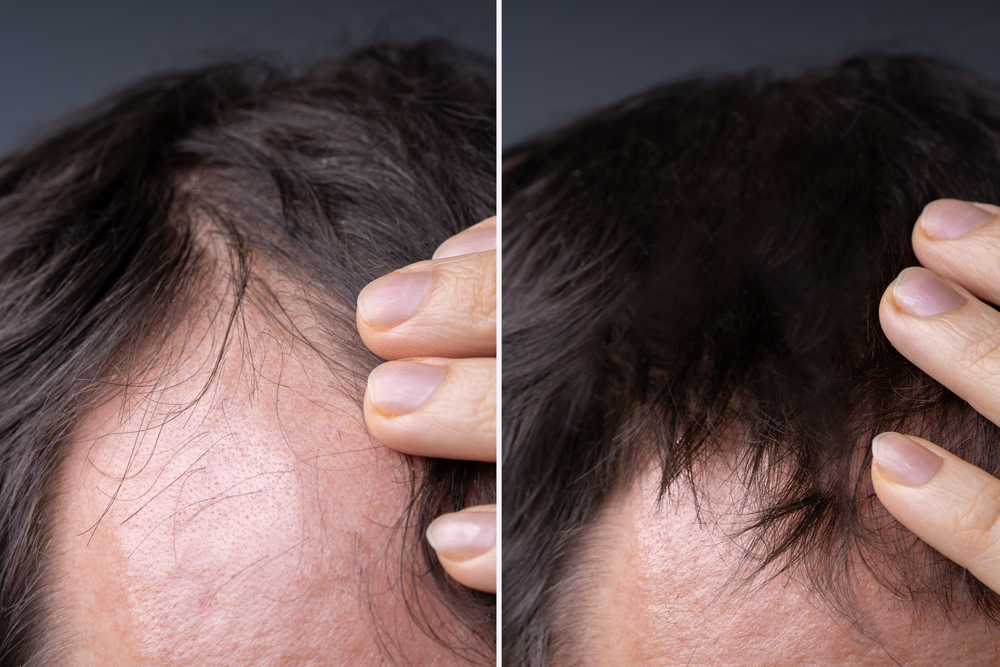
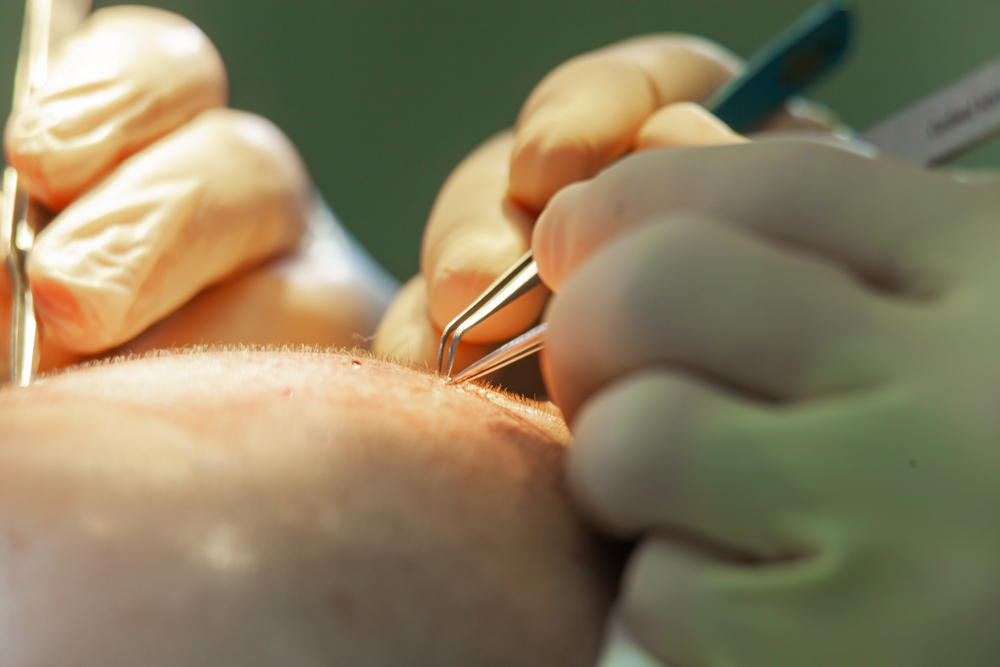
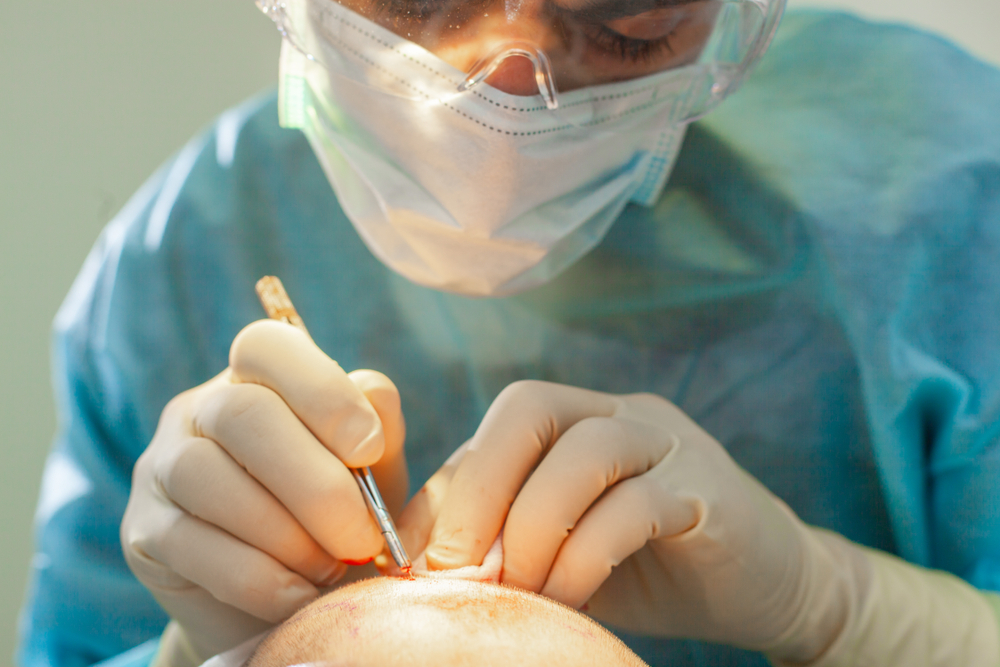
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves taking hair follicles from one area of the body (typically the back or sides of the scalp, which are resistant to hair loss) and transplanting them to an area with thinning or balding hair. The transplanted hair follicles are typically genetically resistant to the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is responsible for male and female pattern baldness. The transplanted hair tends to be more permanent and less likely to fall out over time compared to the hair in the recipient area.
While hair transplants can provide a long-lasting solution to hair loss, they do not necessarily prevent further hair loss from occurring in other areas of your scalp. Hair loss can continue to progress in untreated areas that are genetically predisposed to it. It is possible to go bald again in areas of your scalp that were not treated with a hair transplant.
To maintain the best results and minimize the risk of further hair loss, you can incorporate finasteride or minoxidil into your regular hair care regimen. You may opt for additional hair transplant procedures or other hair restoration treatments if needed.
Consult with a qualified hair transplant surgeon or dermatologist to discuss your specific situation, expectations, and potential treatment options to address any concerns about hair loss after a transplant.